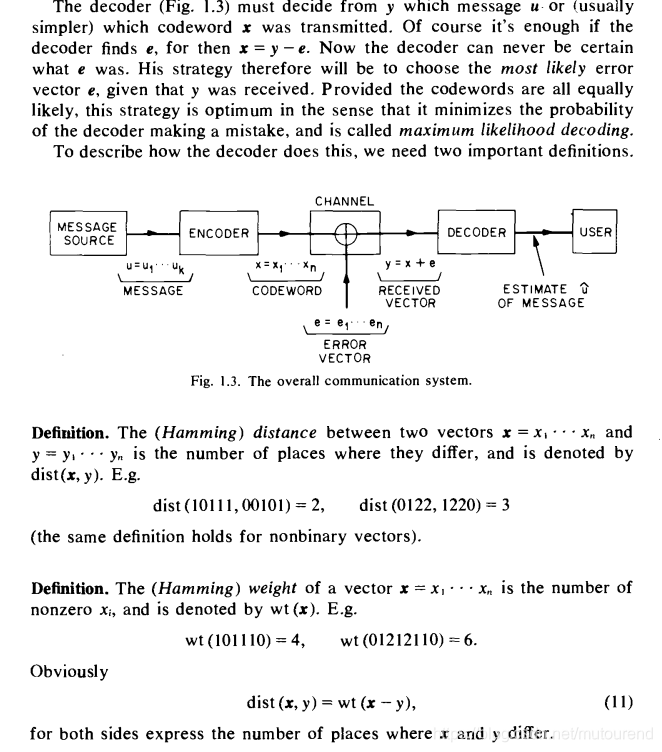
1)理想的传输模型示例: 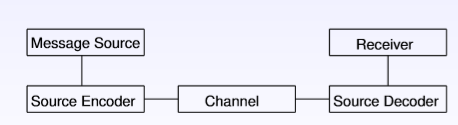
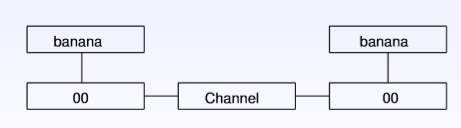 2)实际的传输模型为:
2)实际的传输模型为: 
 3)带纠错功能的传输模型为:
3)带纠错功能的传输模型为: 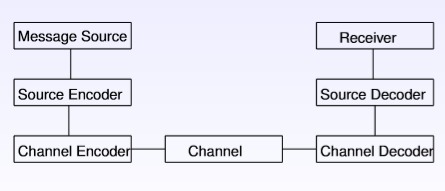
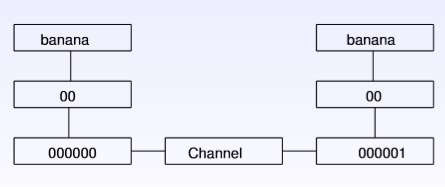 纠错码(error correcting code),在传输过程中发生错误后能在收端自行发现或纠正的码。纠错码常用于保证信息在noisy channel的可靠传输以及保证信息在媒介上的可靠存储(可能会随着时间partially corrupted或者说相应的reading device is subject to errors)。 仅用来发现错误的码一般常称为检错码。检错码与其他手段结合使用,可以纠错。 为使一种码具有检错或纠错能力,须对原码字增加多余的码元,以扩大码字之间的差别 ,即把原码字按某种规则变成有一定剩余度(见信源编码)的码字,并使每个码字的码之间有一定的关系。关系的建立称为编码。码字到达收端后,可以根据编码规则是否满足以判定有无错误。当不能满足时,按一定规则确定错误所在位置并予以纠正。纠错并恢复原码字的过程称为译码。
纠错码(error correcting code),在传输过程中发生错误后能在收端自行发现或纠正的码。纠错码常用于保证信息在noisy channel的可靠传输以及保证信息在媒介上的可靠存储(可能会随着时间partially corrupted或者说相应的reading device is subject to errors)。 仅用来发现错误的码一般常称为检错码。检错码与其他手段结合使用,可以纠错。 为使一种码具有检错或纠错能力,须对原码字增加多余的码元,以扩大码字之间的差别 ,即把原码字按某种规则变成有一定剩余度(见信源编码)的码字,并使每个码字的码之间有一定的关系。关系的建立称为编码。码字到达收端后,可以根据编码规则是否满足以判定有无错误。当不能满足时,按一定规则确定错误所在位置并予以纠正。纠错并恢复原码字的过程称为译码。
纠错码的典型应用是:将message切分为小的blocks,每个block单独编码,当只对某部分信息感兴趣时,可仅解码相应的部分即可。这种策略的优点是:可保证random-access retrieval of information的效率。缺点是:抗噪能力比较弱,哪怕仅有一个block completely corrupted了,相应的信息也就完全丢失了。
提高抗噪能力的一种办法是:对整个message使用纠错码进行编码(encode the whole message into a single codeword of an error-correcting code)。这种策略抗噪能力是增强了,但是当某人仅对某一部分信息感兴趣时,也需要恢复整个message。当面对的是现代的大数据集时,对应的解码复杂度也是令人难以接受的。
1.1 线性纠错码Linear code 其中的
k
k
k为the dimension of the code,
n
n
n为the block length of the code。Linear code需要用
n
n
n个符号来传递
k
k
k长的message,相应的效率
R
=
k
/
n
R=k/n
R=k/n。
其中的
k
k
k为the dimension of the code,
n
n
n为the block length of the code。Linear code需要用
n
n
n个符号来传递
k
k
k长的message,相应的效率
R
=
k
/
n
R=k/n
R=k/n。 
 A linear code of length
n
n
n, dimension
k
k
k,and minimum distance
d
d
d will be called an
[
n
,
k
,
d
]
[n,k,d]
[n,k,d] code. 其中
d
=
m
i
n
d
i
s
t
(
u
⃗
,
v
⃗
)
=
m
i
n
w
t
(
u
⃗
,
v
⃗
)
,
w
h
e
r
e
u
⃗
!
=
v
⃗
d=min\ dist(\vec{u},\vec{v})=min\ wt(\vec{u},\vec{v}), where\ \vec{u}!=\vec{v}
d=min dist(u
,v
)=min wt(u
,v
),where u
!=v
。
A linear code of length
n
n
n, dimension
k
k
k,and minimum distance
d
d
d will be called an
[
n
,
k
,
d
]
[n,k,d]
[n,k,d] code. 其中
d
=
m
i
n
d
i
s
t
(
u
⃗
,
v
⃗
)
=
m
i
n
w
t
(
u
⃗
,
v
⃗
)
,
w
h
e
r
e
u
⃗
!
=
v
⃗
d=min\ dist(\vec{u},\vec{v})=min\ wt(\vec{u},\vec{v}), where\ \vec{u}!=\vec{v}
d=min dist(u
,v
)=min wt(u
,v
),where u
!=v
。
最小距离
d
d
d与可correct errors的关系为: 
maximum likelihood decoding: 最大释然解码。 nearest neighbor decoding:最近邻解码。 由于error vector e ⃗ \vec{e} e 未知,在实际解码时,若 k k k值小,可采用暴力解码的方式将received vector y ⃗ \vec{y} y 与 2 k 2^k 2k个可能的 x ⃗ \vec{x} x 对比,找到最接近的值。但是当 k k k值很大时,暴力解码就不实用了。
1.2 nonlinear code 其中的
M
M
M可表示为
M
=
A
(
n
,
d
)
M=A(n,d)
M=A(n,d)。
其中的
M
M
M可表示为
M
=
A
(
n
,
d
)
M=A(n,d)
M=A(n,d)。
线性与非线性code的表示方法是有差异的。用圆括号()表示的code可为linear或nonlinear,而用中括号[]表示的就是linear code。 linear code [ n , k , d ] [n,k,d] [n,k,d]也可表示为 ( n , 2 k , d ) (n, 2^k,d) (n,2k,d)。 在相同的 d d d的情况下,若希望最终编码的数量 M M M尽可能多,可以用nonlinear code。
常见的nonlinear code有Hadamard code
1.2.1 Hadamard codeHadamard matrix定义如下: 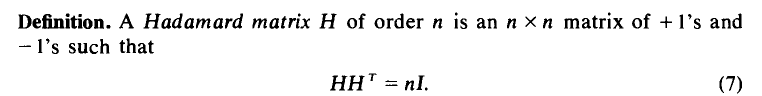
 Normalized Hadamard matric如:
Normalized Hadamard matric如:  若a Hadamard matrix
H
H
H of order
n
n
n exists, then
n
n
n is 1, 2 or a multiple of 4.
若a Hadamard matrix
H
H
H of order
n
n
n exists, then
n
n
n is 1, 2 or a multiple of 4. 
经典的Hadmard code是将 n n n-bit messages编码为 2 n 2^n 2n-bit codewords。 由此可知,Hadmard code的query complexity为2,codeword length exponential in the message length.
 C
H
A
D
C_{HAD}
CHAD的译码流程为:
C
H
A
D
C_{HAD}
CHAD的译码流程为:  C
H
A
D
C_{HAD}
CHAD为2-query
(
2
,
δ
,
2
δ
)
(2,\delta,2\delta)
(2,δ,2δ)-LDC,证明如下:
C
H
A
D
C_{HAD}
CHAD为2-query
(
2
,
δ
,
2
δ
)
(2,\delta,2\delta)
(2,δ,2δ)-LDC,证明如下: 
 上图中的译码过程,会恢复出所有的原码。当仅需要恢复一个原码而不是完整的所有原码时,---->于是有了LDC(Locally Decodable Code)。
上图中的译码过程,会恢复出所有的原码。当仅需要恢复一个原码而不是完整的所有原码时,---->于是有了LDC(Locally Decodable Code)。
Locally DECODABLE CODE是纠错码的一种,LDC既满足了抗噪性的要求,同时也能提供高效的random-access retrieval。( allowing reliablereconstruction of an arbitrary bit of the message from looking at only a small number of randomly chosen codeword bits) LDC牺牲了码字效率,需要更长的码字长度。  LDC不仅可用于可靠传输和可靠存储,还可用于其它领域,如:cryptography, complexity theory, data structures, derandomization, and the theory of fault tolerant computation.
LDC不仅可用于可靠传输和可靠存储,还可用于其它领域,如:cryptography, complexity theory, data structures, derandomization, and the theory of fault tolerant computation.
Locally decodable codes can be seen as the combinatorial analogs of self-correctors [70, 21] that have been studied in complexity theory in the late 1980s. LDCs were also explicitly discussed in the PCP literature in early 1990s, most notably in [6, 88, 80]. However the fifirst formal defifinition of LDCs was given only in 2000 by Katz and Trevisan [64]. See also Sudan et al. [90]. Since then the study of LDCs has grown into a fairly broad fifield.
2.1 LDC定义LDC的具体定义如下: 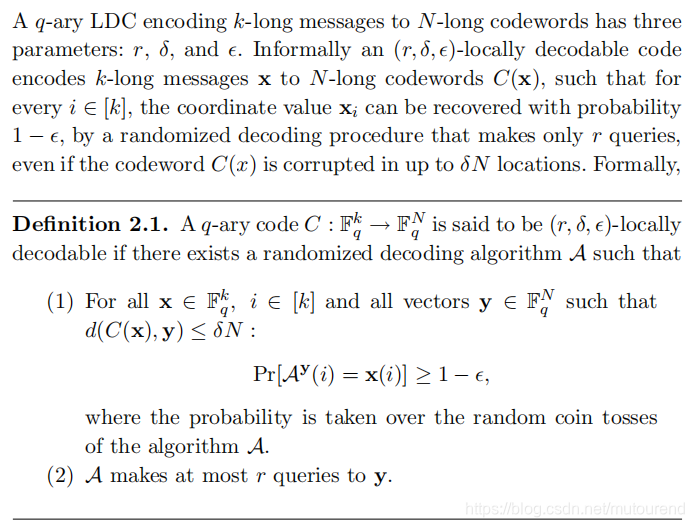 根据以上定义可知,对于
k
k
k-bit长的message,编码后为
q
−
q-
q−进制字母表的情况,我们希望
r
(
代
表
q
u
e
r
y
次
数
,
r
<
<
k
)
,
N
(
代
表
编
码
后
的
长
度
)
,
ϵ
(
代
表
解
码
准
确
率
)
r(代表query次数,r
根据以上定义可知,对于
k
k
k-bit长的message,编码后为
q
−
q-
q−进制字母表的情况,我们希望
r
(
代
表
q
u
e
r
y
次
数
,
r
<
<
k
)
,
N
(
代
表
编
码
后
的
长
度
)
,
ϵ
(
代
表
解
码
准
确
率
)
r(代表query次数,r



