1. 引言
当今的抗量子密钥交换和签名方案依赖于以下假设:
- Learning With Errors(LWE)及其algebraic 变种
- Learning with Rounding(LWR)及其algebraic 变种
其中包含了NIST PQC进程中6个finalists的3个。
当今,对以上假设最有名的密码学分析技术为:
- primal lattice attack
- dual lattice attack
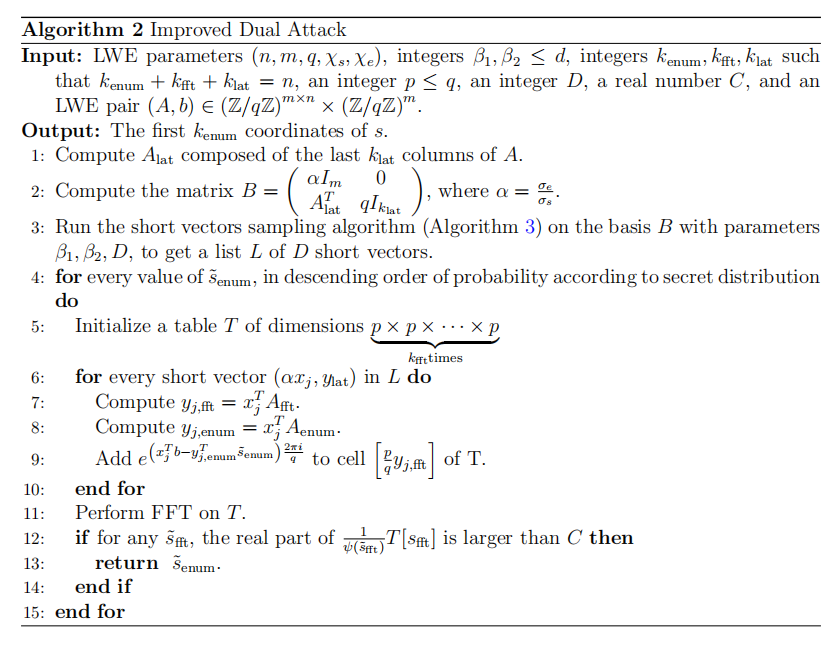
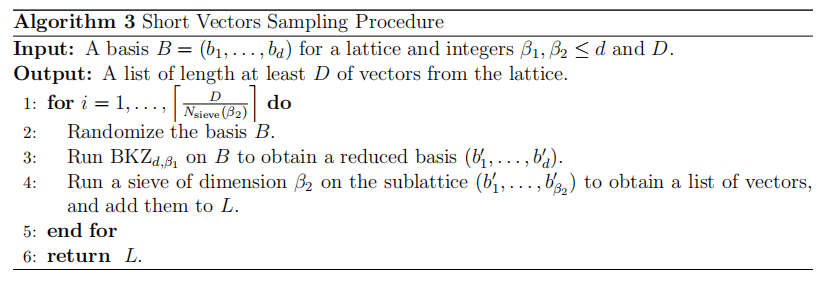
以色列科技公司MATZOV对当今领先的抗量子密码学(Post-Quantum Cryptography,PQC)方案进行了分析,其Improved Dual Lattice Attack:
- 对Dual Lattice Attack算法进行了改进
- 枚举了secret的更多坐标
- 使用了改进的基于FFT的distinguisher
- 改进了在RAM模式下运行lattic sieve所预估的cost
- 降低了解码random product code的门数量
- 执行更少的inner product计算
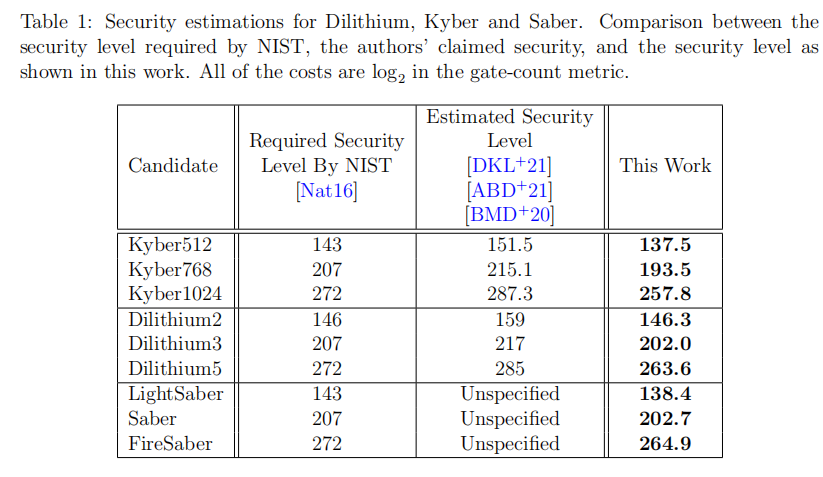
会使基于LWE/LWR finalisits的Kyber、Saber、Dilithium的安全级别低于NIST定义的阈值。

[1] Improved Dual Lattice Attack [2] Report on the Security of LWE: Improved Dual Lattice Attack



