定义在java.lang.Override中,此注释只适用于修辞方法,表示一个方法声明打算重写超类中的另一个方法声明。

定义在java.lang.Deprecated中,此注释可以用于修辞方法,属性,类,表示不鼓励程序员使用这样的元素,通常是因为它很危险或者存在更好的选择。

定义在java.lang.SuppressWarnings中,用来抑制编译时的警告信息。
与前两个注释有所不同,你需要添加一个参数才能正确使用,这些参数都是已经定义好了的,我们选择性的使用就好了。
@SuppressWarnings("all")
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@SuppressWarnings(value={"unchecked","deprecation"})等等


元注解的作用就是负责注解其他注解,Java定义了4个标准的meta-annotation类型,他们被用来提供对其他annotation类型作说明。
这些类型和它们所支持的类在java.lang.annotation包中可以找到(@Target,@Retention, @Documented,@Inherited)
@Target:用于描述注解的使用范围(即:被描述的注解可以用在什么地方)



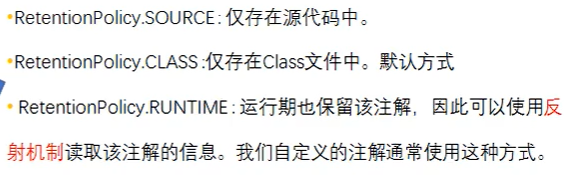
@Retention:表示需要在什么级别保存该注释信息,用于描述注解的生命周期(source < class < runtime)
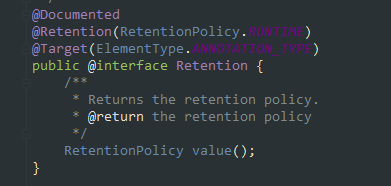

@Document:说明该注解将被包含在javadoc中
@Inherited:说明子类可以继承父类中的该注解

import java.lang.annotation.*;
@MyAnnotation
public class MetaAnnotaion {
@MyAnnotation
public void Test() {
}
}
//定义一个注解
//Target 表示我们的注解可以用在哪些地方
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
//Retention 表示我们的注解在什么地方还有效
// runtime > class > sources 一般用runtime
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//Documented 表示是否将我们的注解生成在JavaDoc中
@Documented
//Inherited 子类可以继承父类的注解
@Inherited
@interface MyAnnotation{}使用@interface自定义注解时,自动继承了java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口
- @interface用来声明一个注解,格式:public@interface注解名{定义内容}
- 其中的每一个方法实际上是声明了一个配置参数
- 方法的名称就是参数的名称
- 返回值类型就是参数的类型(返回值只能是基本类型,Class,String,enum)
- 可以通过default来声明参数的默认值
- 如果只有一个参数成员,一般参数名为value
- 注解元素必须要有值,我们定义注解元素时,经常使用空字符串,0作为默认值
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Java自定义注解
*/
public class Main {
//注解可以显示赋值,如果没有默认值,我们就必须给注解赋值
@MyAnnotation1(age = 18, name = "jak")
public void test1(){}
@MyAnnotation2(value = "1")
public void test2(){}
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation1{
//注解的参数: 参数类型 + 参数名();
String name() default "";
int age();
int id() default -1; // 如果默认值为-1,代表不存在
String[] schools() default {"清华大学", "北京大小"};
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@interface MyAnnotation2{
String value();
}
四、自定义注解实战

import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
//练习反射操作注解
public class TestORM {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException {
Class clazz = Student.class;
//通过反射获得注解
Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
//获得注解的value的值
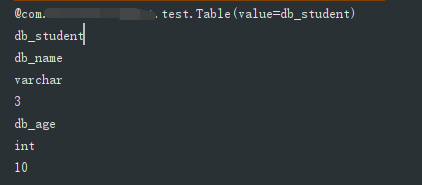
Table table = (Table) clazz.getAnnotation(Table.class);
String value = table.value();
System.out.println(value);
//获得类指定的注解
java.lang.reflect.Field f = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");
Field annotation = f.getAnnotation(Field.class);
System.out.println(annotation.column());
System.out.println(annotation.type());
System.out.println(annotation.length());
//获得类指定的注解
java.lang.reflect.Field f1 = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
Field annotation1 = f1.getAnnotation(Field.class);
System.out.println(annotation1.column());
System.out.println(annotation1.type());
System.out.println(annotation1.length());
}
}
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
@AllArgsConstructor
@Table("db_student")
class Student {
@Field(column = "db_id", type = "int", length = 10)
private int id;
@Field(column = "db_age", type = "int", length = 10)
private int age;
@Field(column = "db_name", type = "varchar", length = 3)
private String name;
}
//类名的注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Table {
String value();
}
//属性的注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Field{
String column();
String type();
int length();
}
教程,参考



