转载 https://blog.csdn.net/manmanxiaowugun/article/details/90170193 还可参考 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/42630740
最近在看图算法相关的东西,先介绍一个用于其中的采样算法吧(超小声的说一句,我打算以后把看过的算法都实现一遍,提高一下工程能力)。
1. 什么叫离散分布首先,离散分布:给你一个概率分布,是离散的,比如[1/2, 1/3, 1/12, 1/12],代表某个变量属于事件A的概率为1/2, 属于事件B的概率为1/3,属于事件C的概率为1/12,属于事件D的概率为1/12。
2. 时间复杂度为o(N)的采样算法首先将其概率分布按其概率对应到线段上,像下图这样:

接着产生0~1之间的一个随机数,然后看起对应到线段的的哪一段,就产生一个采样事件。比如落在0~ 1/2之间就是事件A,落在1/2~5/6之间就是事件B,落在5/6~11/12之间就是事件C,落在11/12~1之间就是事件D。 构建线段的时间复杂度为o(N),如果顺序查找线段的话,查找时间复杂度为o(N),如果二分查找的话,查找的时间复杂度为O(logN)。
3. 时间复杂度O(1)的采样算法——aliasalias分为两步:
1. 做表:
将概率分布的每个概率乘上N,画出柱状图。
其总面积为N,可以看出某些位置面积大于1某些位置的面积小于1,将面积大于1的事件多出的面积补充到面积小于1对应的事件中,以确保每一个小方格的面积为1,同时,保证每一方格至多存储两个事件,这样我们就能看到一个1*N的矩形啦。
表里面有两个数组,一个数组存储的是事件i占第i列矩形的面积的比例,另一个数组存储第i列中不是事件i的另一个事件的编号。
做表的时间复杂度是o(N)。
2. 根据表采样:
先生成一个0到N间的随机整数i,代表选择第i列;
再生成一个0到1间的随机数,若其小于事件i占第i列矩形的面积的比例,则表示接受事件i,否则,接收第i列中不是事件i的另一个事件。
其实你可以算下这种方式事件i的概率,完全对应原来的概率分布。
采样的时间复杂度为 o(1) 。
4. alias 可行性证明Alias 表一定存在吗,为什么做表的的时间复杂度是o(N)? 每一轮只要有小于1的面积,就一定有大于1的面积,则一定可以用大于1的面积那部分把小于1部分给填充到1,这样就进入到了第n+1轮,而且这样每一轮都可以合成一个等于1的面积。
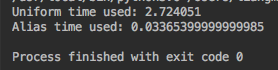
5. 全部代码6. 时间对比
参考网址:
https://blog.csdn.net/haolexiao/article/details/65157026
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/54867139





